
Welcome to AMD ROCm™ Platform¶
AMD ROCm is the first open-source software development platform for HPC/Hyperscale-class GPU computing. AMD ROCm brings the UNIX philosophy of choice, minimalism and modular software development to GPU computing.
Since the ROCm ecosystem is comprised of open technologies: frameworks (Tensorflow / PyTorch), libraries (MIOpen / Blas / RCCL), programming model (HIP), inter-connect (OCD) and up streamed Linux® Kernel support – the platform is continually optimized for performance and extensibility. Tools, guidance and insights are shared freely across the ROCm GitHub community and forums.
Note: The AMD ROCm™ open software platform is a compute stack for headless system deployments. GUI-based software applications are currently not supported.
AMD ROCm is built for scale; it supports multi-GPU computing in and out of server-node communication through RDMA. AMD ROCm also simplifies the stack when the driver directly incorporates RDMA peer-sync support.
The AMD ROCm Programming-Language Run-Time¶
The AMD ROCr System Runtime is language independent and makes heavy use of the Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA) Runtime API. This approach provides a rich foundation to execute programming languages, such as HIP and OpenMP.
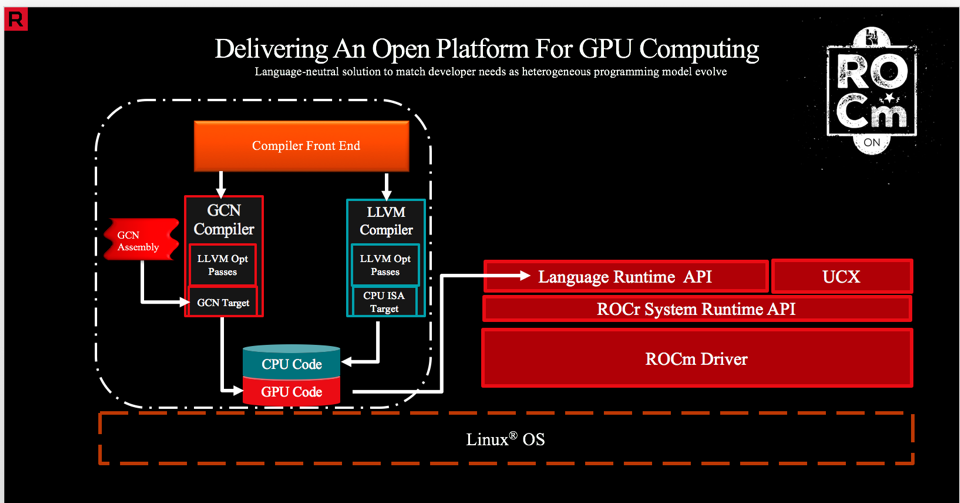
Important features include the following:
Multi-GPU coarse-grain shared virtual memory
Process concurrency and preemption
Large memory allocations
HSA signals and atomics
User-mode queues and DMA
Standardized loader and code-object format
Dynamic and offline-compilation support
Peer-to-peer multi-GPU operation with RDMA support
Profiler trace and event-collection API
Systems-management API and tools
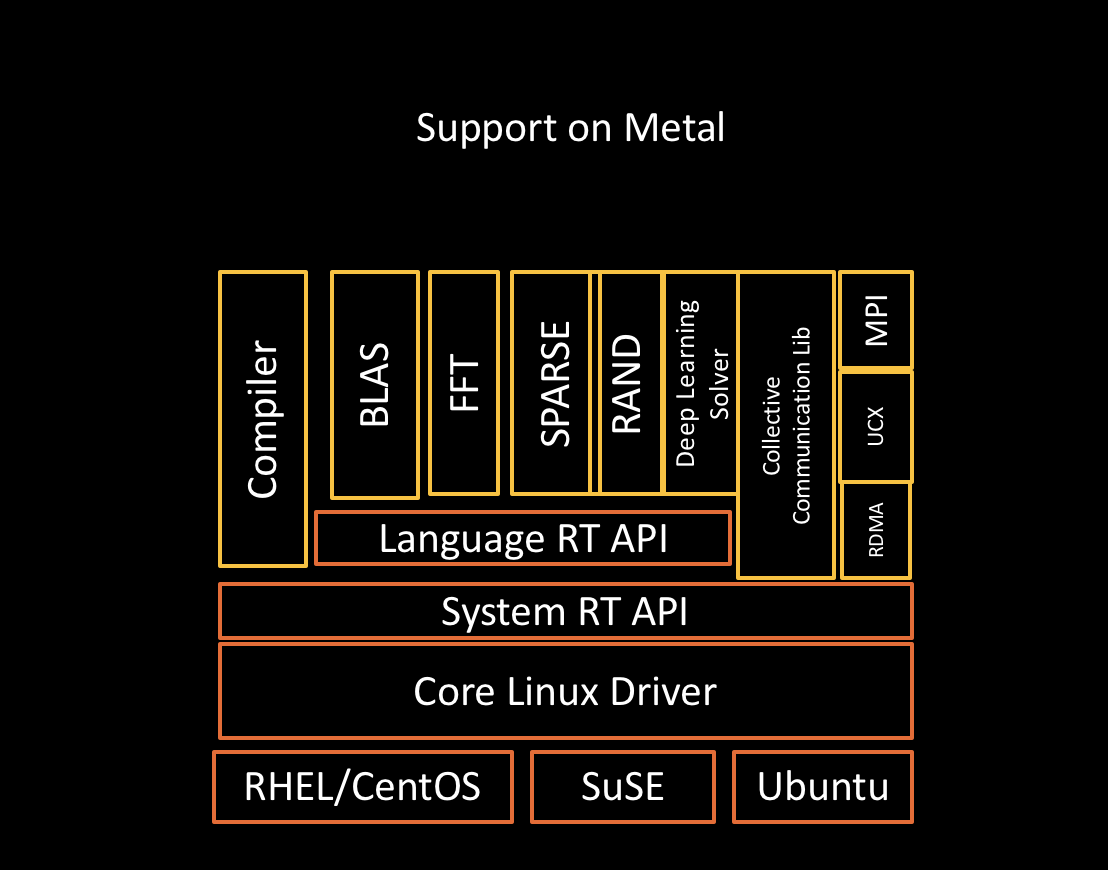
Solid Compilation Foundation and Language Support¶
LLVM compiler foundation
HIP for application portability
GCN assembler and disassembler
AMD ROCm gives developers the flexibility of choice for hardware and aids in the development of compute-intensive applications.